Bolts are the most used fastening materials for pipes in steel piping. They can be without head i.e. studs or with hexagonal heads i.e. machine bolts. They can be either fully threaded or partially threaded.
Tags : #Piping_Engineering #Piping_Fittings #Bolting

As per ASME B16.5, one can use either square head machine bolts or studs for making a joint.
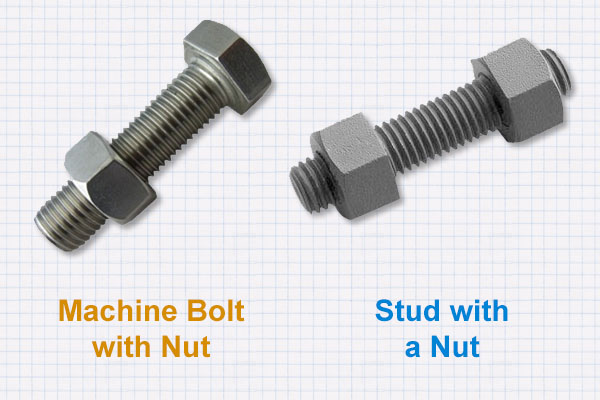
Also, studs are preferred over bolts due to ease of insertion during assembly. At places, like bolting of two valves together, there may not be sufficient clearance available for inserting bolts due to valve body contour and use of studs is the only possible solution.
[google-square-ad]
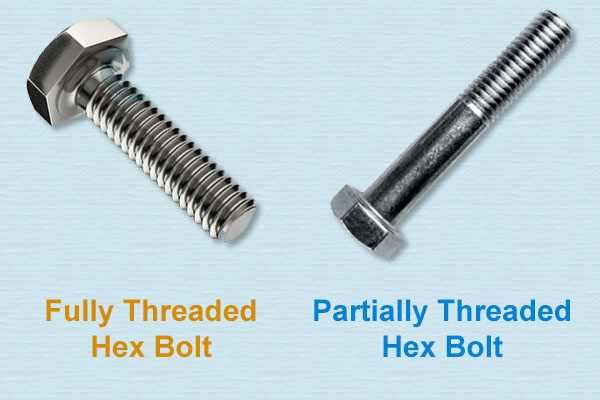
Threading
Bolts and studs are available in either fully threaded or partially threaded condition. The fully threaded structure ensures an equal distribution of elongation when the bolts are tightened and avoid concentration of stresses that exist in partially threaded stock due to varying cross-sections.

Material of Construction
Since bolting material does not come in contact with fluid, its material compatibility with fluid is not important. The selection of bolt material is determined based on service conditions and it is wasteful to specify expensive alloys when carbon steel material is entirely suitable. It is important for bolting material to have good tensile stress.
For carbon steel flanges on process and critical services involving medium and moderately high pressures and temperatures, bolts / studs conforming to ASTM A193 Gr. B7 along with heavy hexagonal head nuts conforming to ASTM A194 Gr. 2H are usually used.
For low temperature carbon steel flanges, studs conforming to ASTM A320 Gr. L7 along with nuts conforming to ASTM A194 Gr. 4 are usually used.
Strengths of Bolts
As per ASME B16.5, bolting material has been divided into three categories :
- High Strength Bolting,
- Intermediate Strength Bolting and
- Low Strength Bolting.
Table 1B of ASME B16.5 Provides list of materials in each of these three categories.
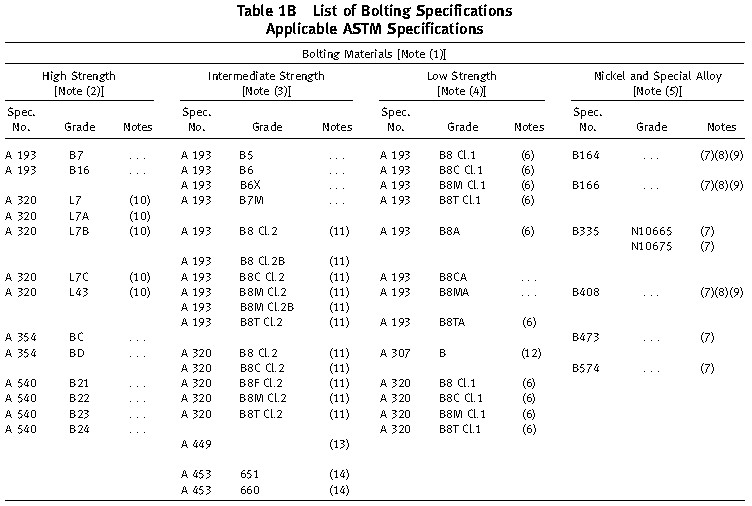
High Strength Bolts
Bolting materials having allowable stresses not less than those for ASTM A193 grade B7 are listed as high strength bolts. Comparable strength material can be used as per Table 1B.
Intermediate Strength Bolts
Bolting materials listed as intermediate strength in Table 1B, and other bolting of comparable strength, may be used in any flanged joint, provided the user verifies their ability to seat the selected gasket and maintain a sealed joint under expected operating conditions.
Low Strength Bolts
Bolting materials having not more than 30 ksi specified minimum yield strength are listed as low strength in Table 1B. These materials and others of comparable strength shall be used only in Classes 150 and 300 joints, and only with gaskets of group no. 1a. Flanged joints using low strength carbon steel bolts shall not be used above 400°F or below -20°F.
[google-square-ad]
Bolts for Plastic Piping
For all flange joints in plastic piping, low strength bolts / studs are usually acceptable. Use of washers is recommended for joints in plastic piping.

Coated Bolts for Corrosive Services
Sometimes in plastic piping, handling corrosive fluids, it is recommended that the fasteners are supplied with cadmium plating or galvanized coating. This is in order to have corrosion resistance against spillages, etc.

Bolts for Cast Iron Flanges
For flanged joints in piping system where one or both flanges are of cast iron, bolts / studs conforming to ASTM A307 Gr. B and nuts conforming to A194 Gr. 2 are usually used. Also for Non Critical services of Carbon Steel Piping of ASME 150 Rating.
Dimensional Standards
- ASME B 18.2.1 : Square and Hex Bolts and Screws – Inch Series.
- DIN 976 Type B : Stud Bolts
- DIN 934 : Hex Nuts
- ASME B 18.2.2 : Square and Hex Nuts.
- Male Threads: ASME B 1.1 C1. 2A Coarse series (UNC)
- Female Threads: ASME B 1.1 C1. 2A Coarse series
General Notes
Repair welding of bolting material is prohibited.
